Do you invest with a
In this guide, I’m going deep to assess the critical differences between Betterment and Wealthfront that impact your fees and returns.
Learn which one you should pick (and why) to maximize your money for long-term earnings and growth.

Many blogs answer the Betterment vs. Wealthfront debate by comparing an exhaustive list of features – live support, a prettier graph
They’re exhaustive but utterly useless. None of them impact your money!
These features are marketing gimmicks. And Wealthfront and Betterment are very good at marketing.
They’ll release lots of features and services that sound fantastic and makes you think you’re getting something special.
This guide will stripe away all the useless stuff and only review differences that impact your money.
Furthermore, I’ll back up every assessment with real data as proof!
Here’s the 6-step ultimate review of Betterment vs. Wealthfront:
- The algorithm for portfolio optimization (which is superior?)
- Management fees and expense ratio (which is lower?)
- Tax loss harvesting (which saves more money?)
- Availability of alternative funds (what are they + are they worth it?)
- Availability of dividend and value stocks (why choose them?)
- Risk parity (what is it, does it actually provide better returns?)
First up, let’s look at the most critical part of a
#1. Betterment and Wealthfront Algorithms are the Same
How is the algorithm different between Betterment vs Wealthfront?
It turns out that they are the same.
Both Betterment and Wealthfront utilize the Modern Portfolio Theory to allocate your money. That’s it. Don’t listen to any other marketing gimmicks telling you they’re unique.
A quick lesson: Economist Harry Markowitz invented the Modern Portfolio Theory in the 1950s. He won a Nobel Prize because of it. The Modern Portfolio Theory is so famous that it dominates every single finance class across MBA schools today.
In fact, here’s the reality of all robo advisors:
Robo advisors like Betterment and Wealthfront all use the Modern Portfolio Theory to build algorithms. As such, their algorithms vary very little from each other.
When it comes to the most crucial aspect of a
But of course, neither Betterment nor Wealthfront wants you to know this! It makes them interchangeable.
But if the algorithm is the same, does anything else matter? Read on!

Every
So the simple answer to if anything else matters is a sort-of. Nothing matters as much as the algorithm. But other things still make a difference. .
And what are these “other things” that matter? For one, fees.
#2. Betterment vs Wealthfront on Fees (management + expense ratio)
Most people don’t know this. Betterment and Wealthfront charge not one but two types of fees:
- A direct fee that goes back to Betterment or Wealthfront, known as the management fee or advisory fee.
- An indirect fee that goes the index funds, usually Vanguard or iShares, known as the expense ratio.
Betterment and Wealthfront both charge 0.25% management fee today.
#On top of management fees, you pay for the expense ratios of the index funds. Betterment and Wealthfront pick near-identical funds and as such, both charge customers around 0.14% in expense ratio fees.
Betterment vs Wealthfront is tied on fees, each charging 0.25% in management fee and 0.14% in expense ratio, or nearly 0.4% total.
You can lower your management fee via referrals.
For every referral, Wealthfront offers to manage $5,000 of your investment for free forever, whereas, for every three referrals, Betterment offers to manage your entire portfolio for free for one year.
Wealthfront’s incentive is slightly better for smaller investors and those able to invite hundreds of users.
Betterment’s incentive is better for high net worth investors.
But in general, Betterment and Wealthfront are pretty much neck and neck on fees, both management and expense ratio.

#3. Betterment vs Wealthfront on Tax Loss Harvesting
Tax loss harvesting is selling a security at a loss and buying a similar one at the same time. The result is that you can keep your allocation and declare a loss to reduce your taxes. Here’s a short video about it:
Wealthfront and Betterment both offer tax loss harvesting at no extra cost. Betterment provides tax loss harvesting at the index fund level, but Wealthfront
- By providing tax loss harvesting at the stock level
- By adjusting the weight of your holding to better optimize for after-tax returns rather than pre-tax returns.
My Betterment vs Wealthfront review suggests that savings from tax loss harvesting are for the most part insignificant:
- Tax loss harvesting only applies to stock outside of retirement (IRA or 401K) accounts because retirement accounts are tax-deferred or tax-free. Since most Americans have their money in retirement accounts, most Americans can’t take advantage of tax loss harvesting.
- Tax loss harvesting only becomes worthwhile when you have a lot of money invested for a very long time. Based on my estimates, you need a few million dollars of taxable investments to get $3,000 of tax deduction via tax loss harvesting.
Betterment’s research claims that its tax loss harvesting on average improves your return by 0.77%. Wealthfront estimates that its stock-level tax loss harvesting can strengthen your returns by 1.61%, with a margin of error of 3.44%. These estimates are likely twice too optimistic and unreliable from year to year.
If you have a massive amount of taxable wealth, look into tax loss harvesting. But know that the savings are minimal compared to your wealth, so better focus your energy elsewhere.
When you have millions of dollars, many other factors impact returns and growth. Tax loss harvesting is insignificant in comparison. But if you are deciding between Betterment vs Wealthfront, Wealthfront wins on tax loss harvesting.

#4. Betterment vs Wealthfront on Alternative Funds
While Betterment and Wealthfront invest in similar index funds, a few minor differences are worth pointing out.
Betterment allocates your money exclusively across stocks and bonds. Wealthfront, on the other hand, assigns a small (5%) portion of your money to Natural Resources or Real Estate.
Wealthfront claims that natural resources and real estate protect investors from inflation because they are correlated with each other.
Betterment argues that the US stock market already includes real estate. So that any additional real estate exposure would overweight it. Betterment also avoids natural resources because there is no evidence that commodities produce long-term returns.
In this round of Betterment vs Wealthfront, I side with Betterment.
Historical performance suggests real estate does not produce good returns in the long run. And there isn’t enough data to make a judgment on natural resources yet.
#5. Betterment vs Wealthfront on Dividend and Value Stocks
When it comes to investing in US stocks, both Betterment and Wealthfront primarily choose the overall US stock market. However, Wealthfront focuses on dividend stocks whereas Betterment focuses on small and mid-cap value stocks.
Betterment cites data showing that value companies have outperformed growth companies and smaller firms have outpaced larger ones. Therefore, investing in small and mid-cap value stocks should produce better returns.
Wealthfront invests in dividend stocks because they tend to be stable companies that are less cyclical and volatile. Wealthfront also sees dividends as an alternative to buying bonds.
In this round of Betterment vs Wealthfront, I agree with Betterment.
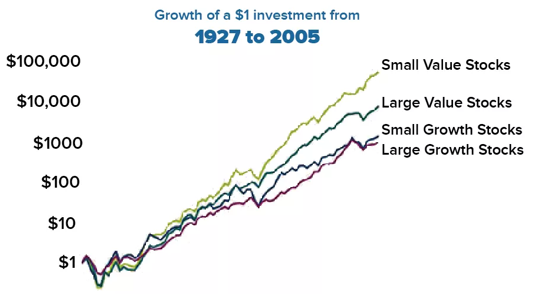
If you are looking to invest and grow your money for the long run, additional exposure to small value stocks
Dividend stocks are not bad, and they may look good because they produce income, but there’s no evidence they outperform the general stock market.
#6. Betterment vs Wealthfront Review: Risky Parity
In 2018, Weathfront launched something big and bold: a new algorithm called Risky Parity.
Risk Parity isn’t new. Wealthfront’s Risk Parity algorithm is a version of the risk parity strategies from hedge funds such as
As of 2018, Risk Parity is available to 20% of your taxable Wealthfront accounts. And by the way, you can always turn Risk Parity off.
Compared to the Modern Portfolio Theory, Risk Parity has a much lower stake in stocks and more exposure to commodities, real estate, and metals. Here’s the best introduction to Risk Parity:
If this sounds a little bit too good to be true, it might be. Risk Parity is relatively new, and every Risk Parity strategy is unique. Very few people understand how it works because the math is very complicated.
In a Wealthfront research paper, Wealthfront backtested its Risk Parity strategy against AQR’s and Bridgewater’s strategies and showed that it performed better by 300 basis points!

But since Wealthfront’s launch of Risk Parity, its actual performance tells the opposite story when compared against AQR’s performance:
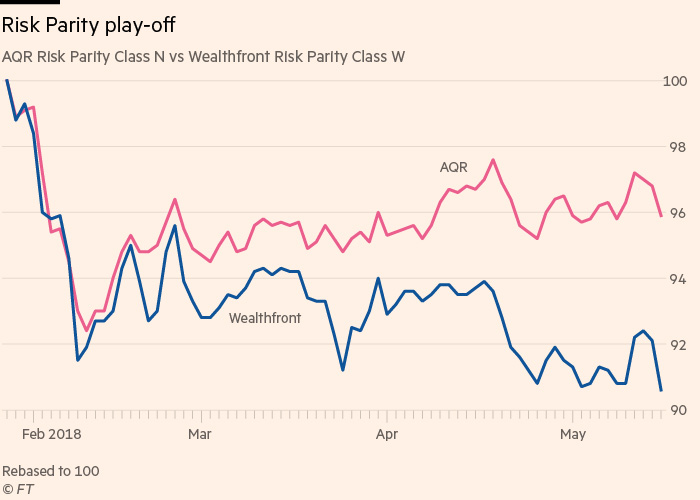
It is hard to conclude anything with only five months of data. But such a wide discrepancy between the hypothetical and the real world should give everyone pause on assuming Risk Parity “just works.”
Final Review: Betterment is the Better Robo Advisor
We see that Betterment and Wealthfront are growing up and growing apart.
Betterment is sticking with the fundamentals of the Modern Portfolio Theory and using only evidence-based strategies.
Wealthfront, on the other hand, is launching newer, fancier, but unproven ways to save money and achieve superior growth.
In the final battle of Betterment
As I manage my parent’s money five years before their retirement, I’m unwilling to gamble on very promising, but ultimately very unproven financial innovations.
However, everyone’s situation is different. I have given Wealthfront some of my money because I have enough taxable cash and I’m still young.
[table id=bvsw /]
Investing in Betterment AND Wealthfront
Also, there is no reason to not invest in both.
Both Betterment and Wealthfront are private companies where there is that added risk of corruption (think Enron) and fraud (think Bernie Madoff). We never believe these risks could occur until they do.
Never put all your eggs in one basket. In this case, never put all your investment with just one
Invest in Betterment today. Use THIS LINK to get your portfolio managed for FREE for 90 days.
Invest in Wealthfront today. Use THIS LINK to get your $5,000 managed for FREE.
Invest Outside of Robo Advisors
I also would not place all my bets with robo advisors. I’d encourage everyone to also invest directly in index funds from Vanguard, Charles Schwab and Fidelity.
Furthermore, invest beyond index funds and venture into actively managed funds with a solid history, such as the Vanguard Wellington Fund and the Wellesley Income Fund. More on this in another post.
Do you agree with my review of Betterment vs Wealthfront? Let me know which robo advisor is your favorite in the comment below!
What’s Next?
Learn more about Betterment in m newly published guide, Betterment Review and Investing Guide of 2019.9
Going beyond
Curious whether this is the right time to invest? Read Will the Stock Market Crash? Complete Analysis
Leave a Reply